1. Introduction
In the organic fertilizer production industry, improving the production capacity of organic fertilizer pelletizers is of great significance for meeting the growing market demand, reducing production costs, and enhancing the competitiveness of enterprises. Organic fertilizer pelletizers are complex mechanical devices, and their production capacity is affected by a variety of factors. Among them, adjusting operation parameters is one of the most direct and effective ways to increase production capacity. By optimizing parameters such as rotation speed, feed rate, and pressure, the performance of the pelletizer can be significantly improved. This article will comprehensively explore how to increase the production capacity of organic fertilizer pelletizers through parameter adjustment.
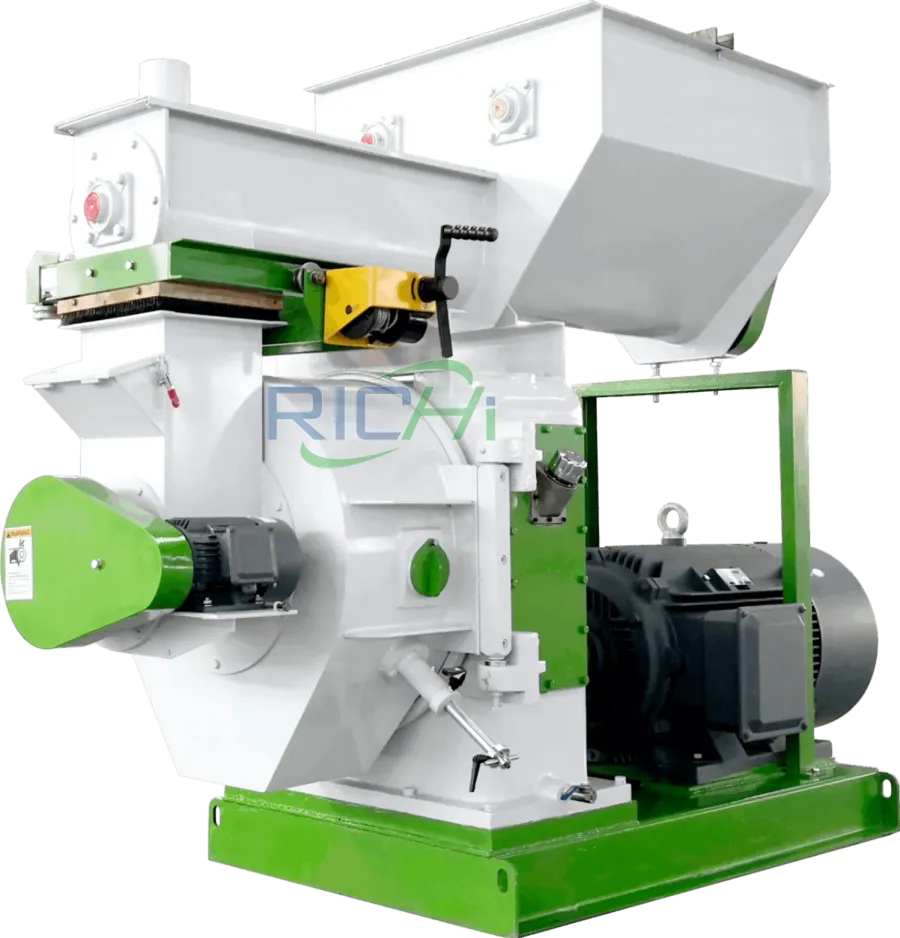

2. Key Parameters Affecting the Production Capacity of Organic Fertilizer Pelletizers
2.1 Rotation Speed
Main Drive Component Rotation Speed
In most organic fertilizer pellet mills, the rotation speed of the main drive components, such as the rollers in compression pelletizers or the screw in extrusion pelletizers, has a crucial impact on production capacity. For compression pelletizers, a higher rotation speed of the rollers can increase the number of times the raw materials are compressed per unit time. However, if the speed is too high, it may cause problems such as uneven compression of the raw materials, increased wear and tear of the rollers and dies, and even affect the quality of the pellets. In extrusion pelletizers, an appropriate increase in the rotation speed of the screw can enhance the material – conveying efficiency, but an overly high speed may lead to overheating of the screw, increased energy consumption, and a decrease in the stability of the extrusion process.
Rotation Speed of Auxiliary Components
In addition to the main drive components, the rotation speed of some auxiliary components also affects production capacity. For example, in disc pelletizers, the rotation speed of the disc determines the movement and agglomeration of the raw materials. A faster – rotating disc can accelerate the formation of pellets, but if the speed is not adjusted properly, it may cause the pellets to be thrown out of the disc due to excessive centrifugal force, reducing the production efficiency.
2.2 Feed Rate
The feed rate of raw materials into the pelletizer is another key parameter. A higher feed rate generally means more raw materials can be processed in a unit of time, which directly increases the production capacity. However, an excessive feed rate may overload the pelletizer. In compression pelletizers, if too much raw material is fed in, the rollers may not be able to compress the materials effectively, resulting in poor – quality pellets and potential damage to the equipment. In extrusion pelletizers, an overly high feed rate can cause blockages in the die, disrupt the extrusion process, and reduce production capacity instead. Therefore, finding the optimal feed rate that matches the processing capacity of the pelletizer is essential. (Related solution:Organic Fertilizer Production Line)
2.3 Pressure
Compression Pressure in Compression Pelletizers
In compression pelletizers, the pressure applied to the raw materials during the compression process is a critical factor. A higher compression pressure can make the pellets more compact and improve their quality. At the same time, appropriate pressure can also increase the production capacity to a certain extent. However, if the pressure is too high, it will not only consume more energy but also accelerate the wear of the rollers and dies, and may even cause the equipment to malfunction. Adjusting the compression pressure according to the characteristics of the raw materials and the desired pellet quality is necessary to balance production capacity and equipment lifespan.
Back – Pressure in Extrusion Pelletizers
In extrusion pelletizers, back – pressure, which is the resistance that the extruded materials encounter when passing through the die, also affects production capacity. An appropriate increase in back – pressure can improve the density and quality of the extruded pellets. However, if the back – pressure is too high, it will increase the load on the screw and the motor, reduce the extrusion speed, and ultimately decrease the production capacity.
3. Strategies for Adjusting Parameters to Increase Production Capacity
3.1 Optimizing Rotation Speed
Experimental Determination of Optimal Speed
To determine the optimal rotation speed, experimental research is often required. First, select a series of different rotation speeds within a reasonable range. For example, for a compression pelletizer, start with a relatively low rotation speed, such as 10 – 15 revolutions per minute (RPM), and gradually increase it in increments of 5 – 10 RPM. At each speed, measure the production capacity, pellet quality (including particle size uniformity, density, and hardness), and observe the operation status of the equipment, such as whether there is abnormal vibration or noise. Through comprehensive analysis of these data, find the rotation speed that can achieve the best balance between production capacity and pellet quality.
Consideration of Raw – Material Characteristics
The characteristics of the raw materials also play a decisive role in determining the rotation speed. If the raw materials are relatively soft and easy to process, a higher rotation speed may be applicable. For example, when using well – composted and fine – textured organic matter as raw materials, the rollers in a compression pelletizer can rotate at a relatively high speed, such as 30 – 40 RPM. However, if the raw materials are hard or contain a large amount of fibrous substances, a lower rotation speed is needed to ensure uniform processing. For instance, when dealing with raw materials with a high content of crop straws, the rotation speed may need to be controlled at around 15 – 20 RPM. (Related project:7-8 T/H Manure Fertilizer Pellet Plant In Senegal)
3.2 Adjusting Feed Rate
Monitoring and Adjusting in Real – Time
To adjust the feed rate effectively, it is necessary to install monitoring devices on the pelletizer. For example, a flowmeter can be installed in the raw – material feeding system to monitor the feed rate in real – time. When starting the production, begin with a relatively low feed rate, such as 50 – 60% of the rated feed rate of the pelletizer. Observe the operation of the pelletizer, such as whether the raw materials can be smoothly processed, and whether there is any sign of overloading. Gradually increase the feed rate in small increments until the pelletizer reaches its maximum stable production capacity. At the same time, closely monitor the quality of the produced pellets to ensure that the increase in feed rate does not lead to a decline in pellet quality.
Matching with Equipment Capacity
The feed rate should be matched with the overall capacity of the pelletizer and its associated equipment. For example, if the conveyor belt that transports the raw materials to the pelletizer has a limited conveying capacity, increasing the feed rate beyond the conveyor’s capacity will cause material accumulation and disrupt the production process. In addition, consider the processing capacity of the post – treatment equipment, such as the cooling and packaging systems. If the feed rate is increased without ensuring that the post – treatment equipment can handle the increased production volume, it will also lead to production bottlenecks.
3.3 Controlling Pressure
Pressure – Sensing and Adjustment Systems
Installing pressure – sensing devices in the pelletizer is crucial for precise pressure control. In compression pelletizers, pressure sensors can be installed on the rollers or dies to monitor the compression pressure in real – time. Based on the sensor data, an automatic pressure – adjustment system can be set up. For example, if the pressure is lower than the set value, the system can automatically increase the hydraulic pressure (if it is a hydraulic – driven compression mechanism) to increase the compression force. In extrusion pelletizers, pressure sensors can be installed near the die to monitor the back – pressure. If the back – pressure is too high, the system can adjust the rotation speed of the screw or the opening degree of the die to reduce the back – pressure.
Adjusting Pressure According to Production Requirements
The pressure should be adjusted according to the specific production requirements. If the goal is to produce high – density pellets for long – distance transportation or for use in certain special applications, a relatively high pressure can be set. However, if the pellets are mainly for local use and a lower density is acceptable, the pressure can be appropriately reduced to save energy and reduce equipment wear. In addition, different raw materials also require different pressure settings. For example, raw materials with a high moisture content may require less pressure to form pellets compared to dry and hard raw materials.
4. Interaction Among Parameters and Overall Optimization
4.1 Interaction Effects
The rotation speed, feed rate, and pressure are not independent parameters but interact with each other. For example, increasing the rotation speed may require an appropriate increase in the feed rate to ensure that the main drive components are fully utilized. However, if the feed rate is increased too much while the rotation speed remains unchanged, it may cause overloading. At the same time, changes in pressure also affect the relationship between rotation speed and feed rate. A higher compression pressure in compression pelletizers may require a lower rotation speed to ensure uniform compression, and a corresponding adjustment of the feed rate is also needed to maintain the balance of the production process.
4.2 Overall Optimization Process
To achieve overall optimization of parameters and maximize production capacity, a systematic approach is needed. First, establish a mathematical model based on experimental data and theoretical analysis to describe the relationship among rotation speed, feed rate, pressure, and production capacity. Then, use optimization algorithms, such as genetic algorithms or simulated annealing algorithms, to find the optimal combination of parameters. During the optimization process, not only the production capacity but also other factors such as energy consumption, pellet quality, and equipment lifespan should be considered. For example, when using genetic algorithms, set the production capacity as the main optimization objective, while adding constraints on energy consumption, pellet quality standards, and equipment wear limits. Through continuous iteration and optimization, the best parameter combination can be obtained.
5. Case Studies of Parameter – Adjustment – Driven Capacity Increase
5.1 Case 1: A Large – Scale Compression – Pelletizer – Based Organic Fertilizer Plant
A large – scale organic fertilizer plant in a certain area used compression pelletizers for production. Initially, the production capacity of the pelletizer was relatively low, unable to meet the market demand. After conducting a series of parameter – adjustment experiments, it was found that the original rotation speed of the rollers was set too low at 15 RPM, and the feed rate was only 40% of the rated value. By gradually increasing the rotation speed to 30 RPM and adjusting the feed rate to 70% of the rated value while optimizing the compression pressure, the production capacity of the pelletizer increased by 60%. At the same time, through strict quality control, the quality of the produced pellets still met the relevant standards.
5.2 Case 2: A Small – Scale Extrusion – Pelletizer – Using Organic Fertilizer Manufacturer
A small – scale organic fertilizer manufacturer using extrusion pelletizers faced production capacity bottlenecks. After installing pressure – sensing and monitoring devices, it was discovered that the back – pressure in the extrusion process was too high, reaching 10 – 15% higher than the optimal value. By adjusting the screw rotation speed from 20 RPM to 25 RPM and slightly increasing the die opening degree to reduce the back – pressure, and at the same time optimizing the feed rate, the production capacity of the extrusion pelletizer increased by about 30%. The quality of the extruded pellets also improved, with more uniform particle sizes and better density.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, adjusting parameters is an effective way to increase the production capacity of organic fertilizer pelletizers. By optimizing key parameters such as rotation speed, feed rate, and pressure, and considering the interaction among these parameters, significant improvements in production capacity can be achieved. Experimental research, real – time monitoring, and the use of optimization algorithms are important means to ensure the effectiveness of parameter adjustment. Case studies have shown that through reasonable parameter adjustment, both large – scale and small – scale organic fertilizer production enterprises can effectively increase the production capacity of their pelletizers, meet market demand, and improve economic benefits. In the future, with the continuous development of technology, more advanced methods for parameter adjustment and production – capacity improvement of organic fertilizer pelletizers are expected to emerge.